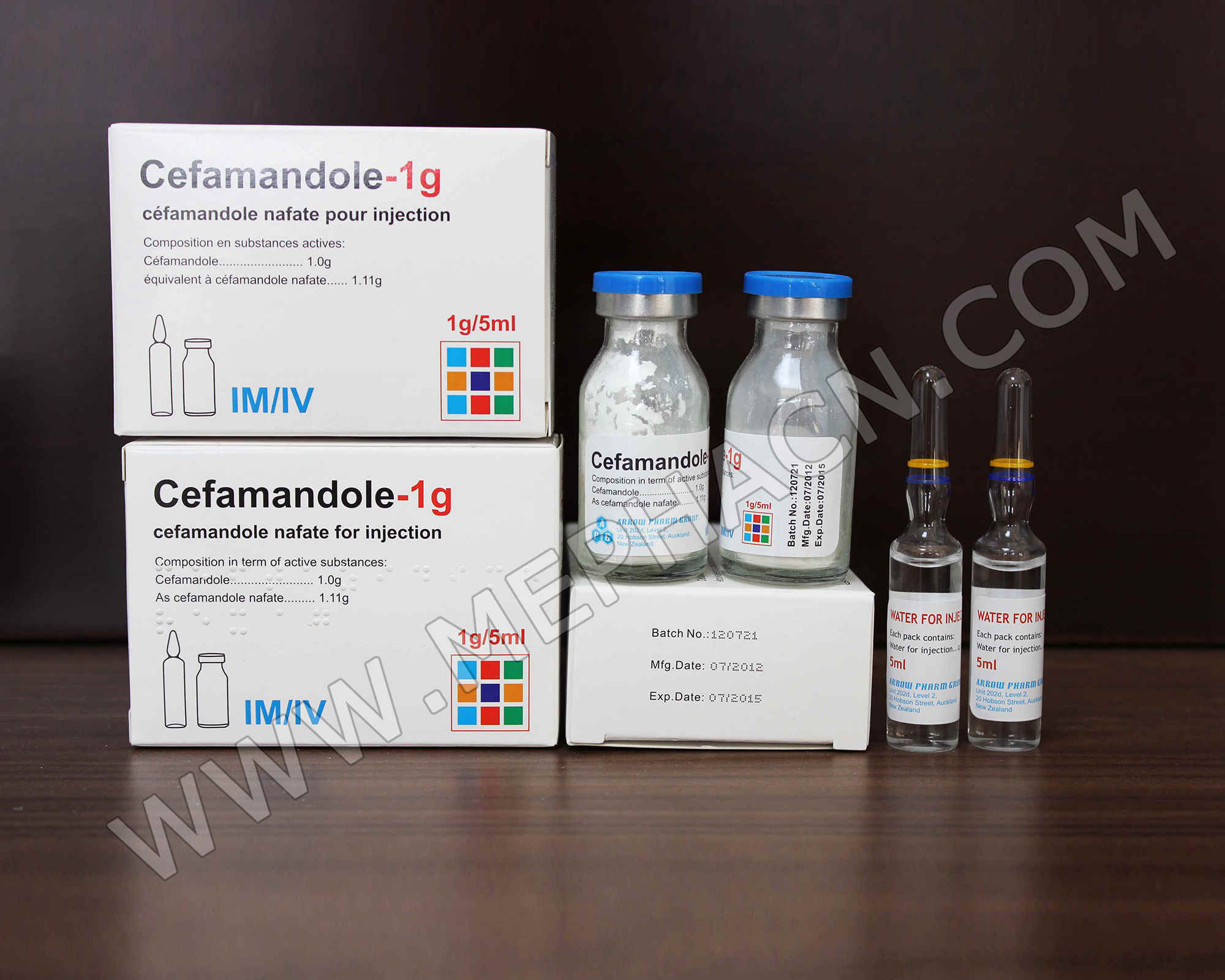
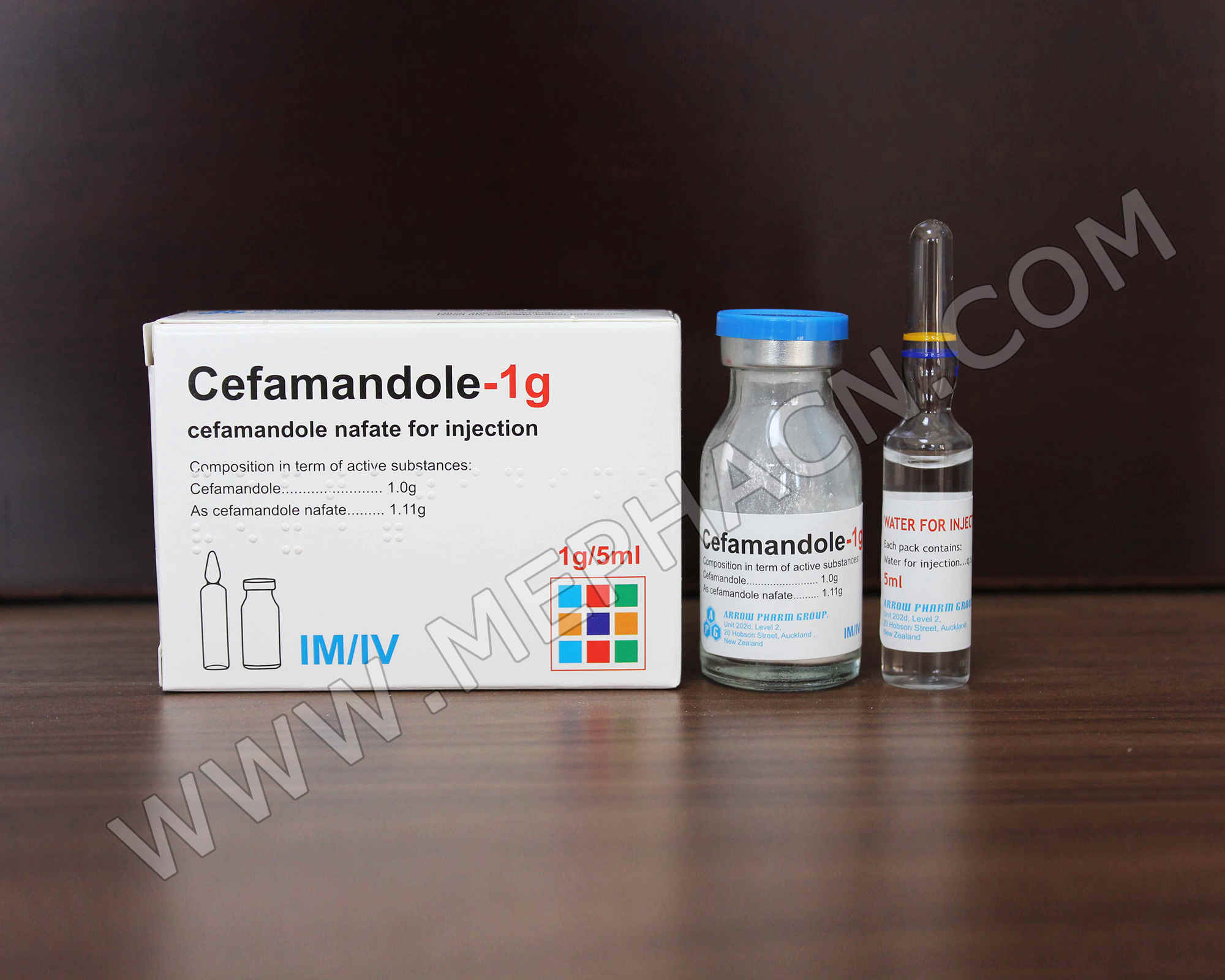
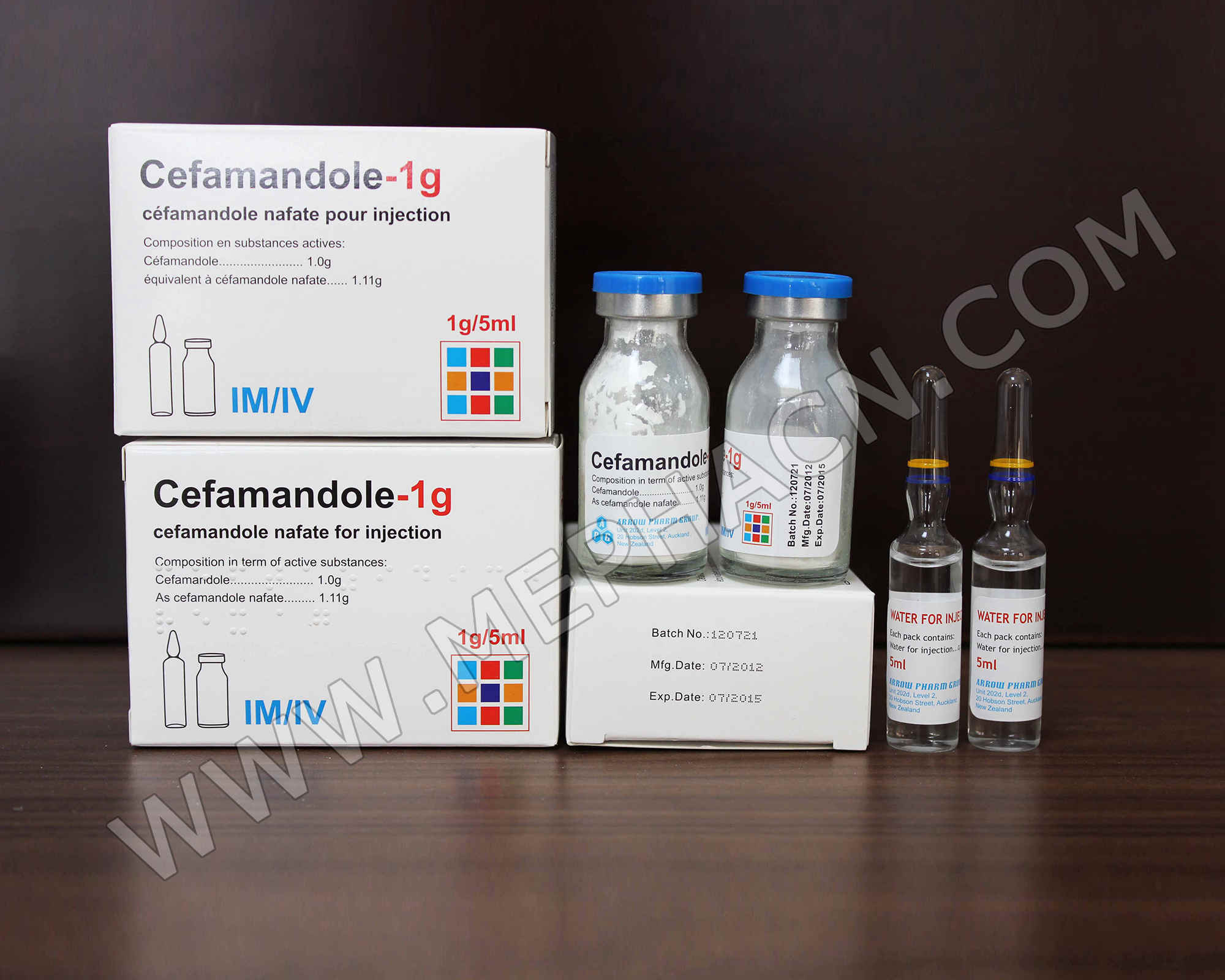
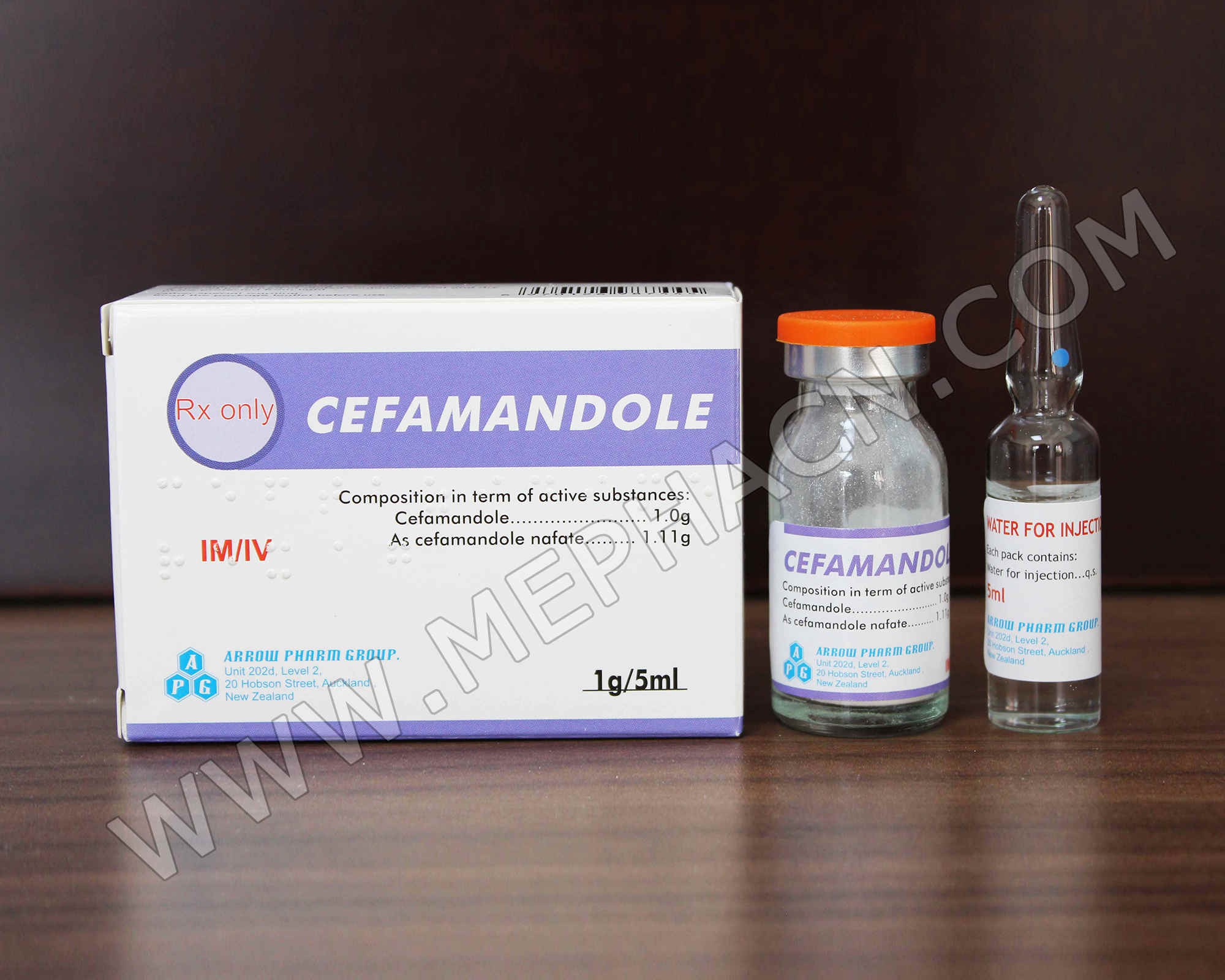
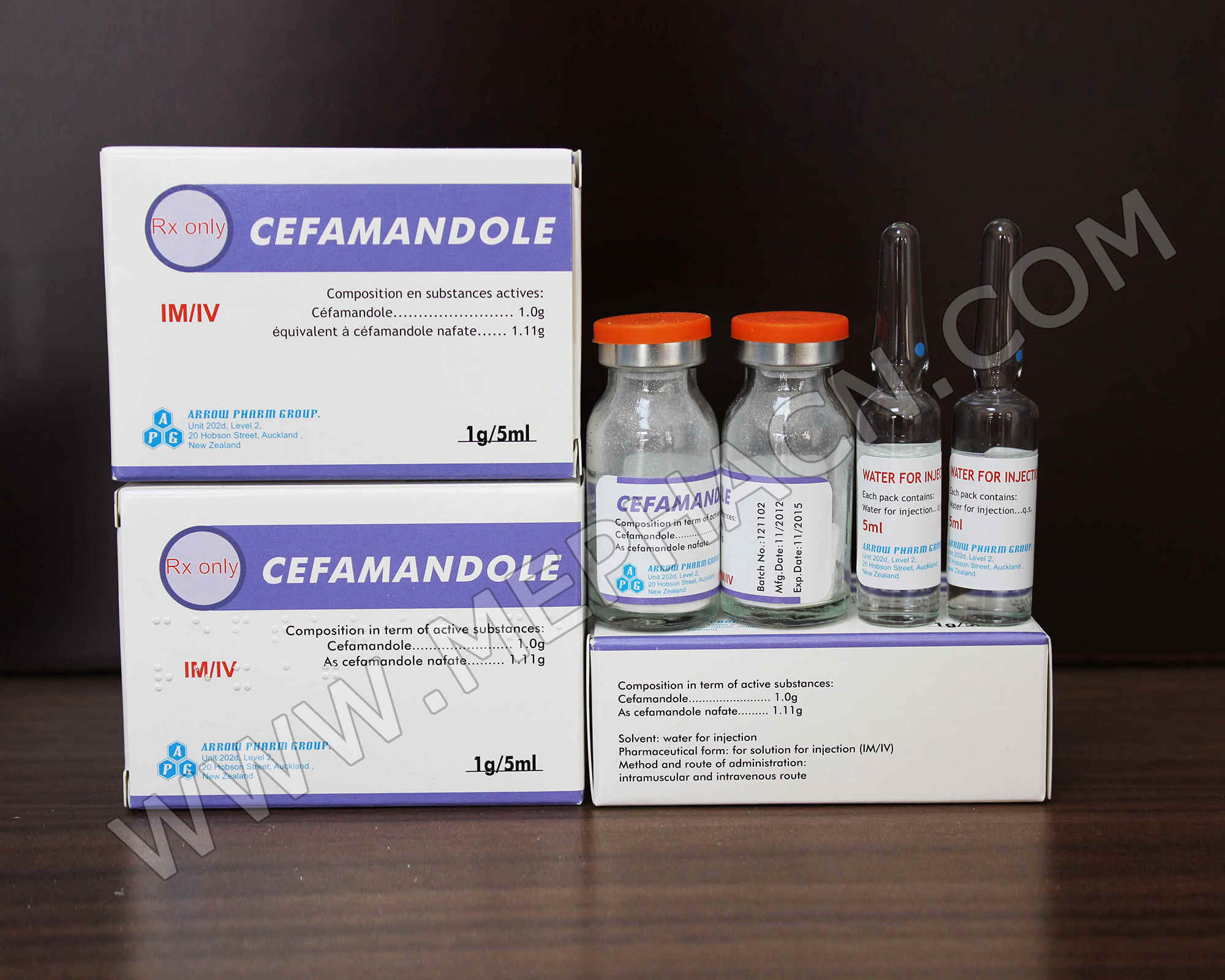
Cefamandole nafate for injection 1g
1. Product name: Cefamandole nafate for injection
2. Specification: 1g/5ml
3. Package: 1 vial+1 solvent/box
4. Shelf life: 36 months
5. Registration dossiers are available.
If you are interested in our products, please feel free to contact us.
1. What Cefamandole nafate for injection is and what it is used for
Cefamandole Nafate for Injection, is a semisynthetic broad-spectrum cephalosporin antibiotic for parenteral administration.Cefamandole is indicated for the treatment of serious infections caused by susceptible strains of the designated microorganisms in the diseases listed below:
2. Before you use Cefamandole nafate for injection
General Although cefamandole rarely produces alteration in function, evaluation of status is recommended, especially in seriously ill patients receiving maximum doses.Prolonged use of cefamandole may result in the overgrowth of nonsusceptible organisms. Careful observation of the patient is essential. If superinfection occurs during therapy, appropriate measures should be taken.
Usage in Pregnancy Pregnancy Category B Reproduction studies have been performed in rats given doses of 500 or 1,000 mg/kg/day and have revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to cefamandole. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers Caution should be exercised when cefamandole is administered to a nursing woman.
3. How to use Cefamandole nafate for injection
Dosage Adults: The usual dosage range for cefamandol (cefamandole) is 500 mg to 1 g every 4 to 8 hours.In infections of skin structures and in uncomplicated pneumonia, a dosage of 500 mg every 6 hours is adequate.
In uncomplicated urinary tract infections, a dosage of 500 mg every 8 hours is sufficient. In more serious urinary tract infections, a dosage of 1 g every 8 hours may be needed.
In severe infections, 1-g doses may be given at 4 to 6-hour intervals.
In life-threatening infections or infections due to less susceptible organisms, doses up to 2 g every 4 hours (ie, 12 g/day) may be needed.
Infants and Children: Administration of 50 to 100 mg/kg/ day in equally divided doses every 4 to 8 hours has been effective for most infections susceptible to cefamandole. This may be increased to a total daily dose of 150 mg/kg (not to exceed the maximum adult dose) for severe infections
4. Possible side effects
Gastrointestinal Symptoms of pseudomembranous colitis may appear either during or after antibiotic treatment. Nausea and vomiting have been reported rarely. As with some penicillins and some other cephalosporins, transient hepatitis and cholestatic jaundice have been reported rarely.Hypersensitivity Anaphylaxis, maculopapular rash, urticaria, eosinophilia, and drug fever have been reported. These reactions are more likely to occur in patients with a history of allergy, particularly to penicillin.
5. Storing Cefamandole nafate for injection
Controlled Room Temperature : 15 to 30( 59 to 86).